Open 7 Days a Week, from 9 AM to 9 PM
Cough, Bronchitis, or Pneumonia? When to Get Checked
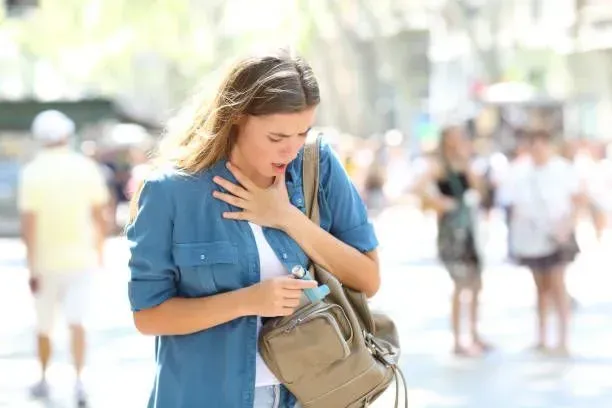
A lingering cough can be frustrating and disruptive. But how do you determine if it’s something minor like a common cold, bronchitis, or a more serious condition like pneumonia? Each of these respiratory illnesses can have overlapping symptoms, making it difficult to tell them apart.
This blog will help you understand the differences between a persistent cough, bronchitis, and pneumonia. Recognize when symptoms warrant medical attention, and explore prevention strategies to keep your lungs healthy.
Understanding the Common Causes of a Persistent Cough
Coughing is your body’s natural defense mechanism to clear irritants, mucus, or foreign particles from your airways. However, a cough that doesn’t improve or worsens over time can indicate an underlying condition.
1. Acute Cough
- Lasts less than three weeks.
- Often caused by viral infections like the common cold or flu.
2. Subacute Cough
- Persists for three to eight weeks.
- Frequently follows respiratory infections and may result from postnasal drip or inflammation.
3. Chronic Cough
- Lasts more than eight weeks.
- Can be due to conditions like asthma, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), or chronic bronchitis.
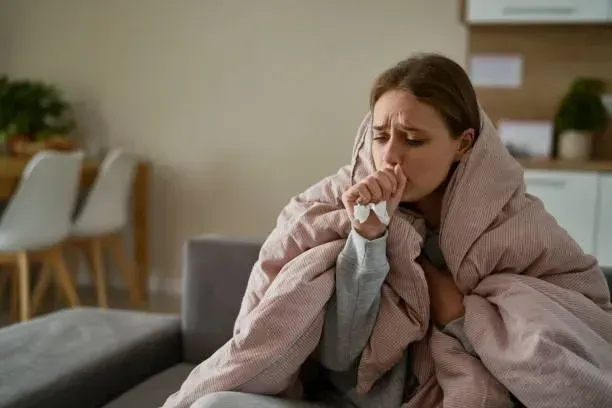
Bronchitis: Inflammation of the Bronchial Tubes
Bronchitis occurs when the bronchial tubes, responsible for carrying air to your lungs, become inflamed. This inflammation leads to swelling and mucus production, causing a characteristic cough.
Types of Bronchitis
- Acute Bronchitis: Often caused by viral infections, lasting about 10–14 days, though the cough may linger longer.
- Chronic Bronchitis: A long-term condition, often associated with smoking or environmental irritants, and classified as a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
Symptoms of Bronchitis
- Persistent cough with mucus production (clear, yellow, or green).
- Chest discomfort or tightness.
- Fatigue due to prolonged coughing.
- Wheezing or shortness of breath.
- Mild fever or chills.
Example: If you recently had a cold and developed a lingering wet cough with yellow mucus, it may be acute bronchitis.

When to Be Concerned:
- The cough persists for more than three weeks.
- You experience significant shortness of breath or wheezing.
- There’s blood in your mucus.
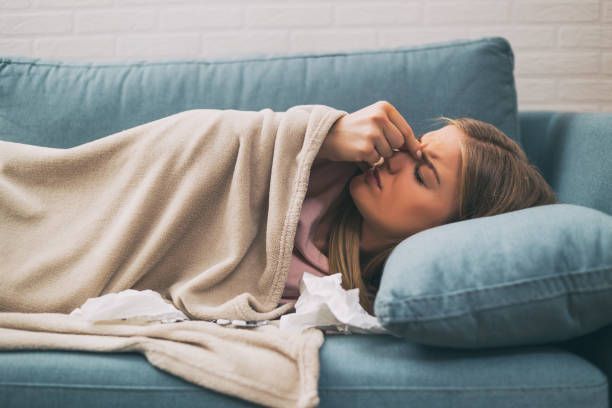
Pneumonia: Infection of the Lungs
Pneumonia is a more severe condition that involves infection of the air sacs in one or both lungs, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup. It can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
- Severe or persistent cough, sometimes with blood-streaked mucus.
- High fever (above 101°F) with chills and sweating.
- Sharp chest pain, often worsening with deep breaths or coughing.
- Difficulty breathing or rapid, shallow breaths.
- Extreme fatigue and weakness.
- Confusion, especially in older adults.
Example: A sudden onset of high fever, chills, and a painful cough after recovering from the flu could indicate bacterial pneumonia.
Risk Factors for Pneumonia:
Age (young children and older adults are more susceptible).- Pre-existing conditions such as asthma, diabetes, or heart disease.
- Smoking or a weakened immune system.
Comparing Bronchitis and Pneumonia
Cause
- Bronchitis: Typically viral in origin.
- Pneumonia: Can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi.
Cough
- Bronchitis: Persistent with mucus production.
- Pneumonia: Severe, may be dry or wet, and can sometimes include blood.
Fever
- Bronchitis: Mild, if present.
- Pneumonia: High fever, often accompanied by chills.
Breathing
- Bronchitis: Mild shortness of breath or occasional wheezing.
- Pneumonia: Significant difficulty in breathing.
Chest Pain
- Bronchitis: Mild discomfort.
- Pneumonia: Sharp, stabbing pain, especially with deep breaths or coughing.
Fatigue
- Bronchitis: Moderate tiredness.
- Pneumonia: Severe fatigue, often making physical activities challenging.
Related blog:
Most Common Conditions Treated in Urgent Care Clinics: A Comprehensive Guide
When Should You Seek Medical Attention?
Determining when to consult a healthcare provider is critical, as untreated pneumonia can lead to serious complications like sepsis or respiratory failure.
Signs That Warrant Immediate Medical Care
Severe Breathing Difficulties:
- Feeling like you can’t catch your breath.
- Rapid breathing or blue-tinged lips.
High Fever and Chills:
- Persistent fever above 102°F that doesn’t respond to medication.
Chest Pain:
- Intense pain that worsens when coughing or breathing deeply.
Confusion or Drowsiness:
- Common in older adults, indicating a lack of oxygen or severe infection.
Cough Producing Blood:
- Bright red or rust-colored mucus is a red flag for pneumonia or other serious conditions.
Persistent Symptoms:
- Cough and fatigue lasting longer than three weeks.
Read this next: Finding Immediate Medical Help: Your Ultimate Guide to Locating the Best Urgent Care Near You

How Bronchitis and Pneumonia Are Diagnosed
Healthcare providers use a combination of medical history, physical exams, and diagnostic tests to differentiate between bronchitis and pneumonia.
1. Medical History
- Questions about symptom duration, triggers, and associated conditions like smoking or recent illnesses.
2. Physical Examination
- Listening to lung sounds with a stethoscope to detect wheezing, crackling, or decreased air entry.
3. Diagnostic Tests
- Chest X-Ray: Essential for diagnosing pneumonia by revealing lung inflammation or fluid.
- Blood Tests: Identify infection markers and differentiate between viral and bacterial causes.
- Sputum Test: Determines the presence of bacteria or fungi in mucus.
Example:
A chest X-ray showing fluid-filled air sacs confirms pneumonia, whereas bronchitis typically doesn’t show structural changes in the lungs.
Treatment Options
1. For Acute Bronchitis
Rest and Hydration: Key for recovery.
Over-the-Counter Remedies:
- Cough suppressants for dry coughs.
- Expectorants to thin mucus for productive coughs.
Inhalers: May be prescribed for wheezing or shortness of breath.
2. For Pneumonia
- Antibiotics: Required for bacterial pneumonia.
- Antiviral Medications: Prescribed for viral pneumonia in severe cases.
- Hospitalization: Necessary for severe cases with oxygen therapy, IV fluids, and intensive monitoring.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing respiratory illnesses like bronchitis and pneumonia begins with strengthening your immune system and minimizing exposure to irritants.
1. Vaccination
- Flu Vaccine: Protects against influenza, a common precursor to bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Pneumococcal Vaccine: Recommended for young children, older adults, and individuals with chronic conditions.
2. Avoid Smoking and Pollutants
Smoking damages lung tissue and increases vulnerability to respiratory infections. Similarly, exposure to air pollutants and workplace irritants can trigger bronchial inflammation.
Example:
Using an air purifier at home can reduce indoor air irritants and improve overall respiratory health.
3. Practice Good Hygiene
- Wash hands regularly to minimize germ spread.
- Avoid close contact with sick individuals.
Example: Carrying hand sanitizer during flu season is an effective preventive measure.
4. Boost Your Immune System
- Eat a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein.
- Exercise regularly to improve lung capacity and circulation.
- Get 7–9 hours of sleep each night.
Example:
Consuming foods high in vitamin C, like oranges and bell peppers, supports immune function and helps fend off infections.
What to Expect at the Doctor's Office
If you seek medical care for a persistent cough or other concerning symptoms, here’s what you can expect:
- Initial Evaluation: The doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle habits (e.g., smoking).
- Lung Examination: Using a stethoscope to listen for abnormal lung sounds.
- Treatment Recommendations:
- For mild bronchitis, you may only need symptomatic care.
- Pneumonia often requires a more aggressive approach, such as antibiotics or hospitalization.
- Follow-Up: Your doctor may schedule a follow-up appointment or chest X-ray to confirm recovery.
Check In With Us at UgiClinic Urgent
Check In With Us at UgiClinic Urgent
Coughing can stem from a range of causes, from mild irritation to serious infections like pneumonia. While acute bronchitis often resolves on its own, pneumonia can lead to life-threatening complications if untreated. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking urgent medical care is crucial for a full recovery.
If you’re experiencing a persistent cough, fever, or difficulty breathing, don’t hesitate to seek urgent medical care.
Check-in with us at Urgiclinic Urgent Care. Your health is worth it.
If you believe you have a medical urgent situation, please call 911
Hours: Open 7 Days a Week, from 9 AM to 9 PM
LEGAL LINKS
Quick Links
Contact Us
Phone: (708) 788-5088
Fax: (708) 575-7177
Email: care@urgiclinic.com
Address: 7124 W 83rd St Unit C, Bridgeview, IL 60455
All Rights Reserved | UrgiClinic Urgent Care